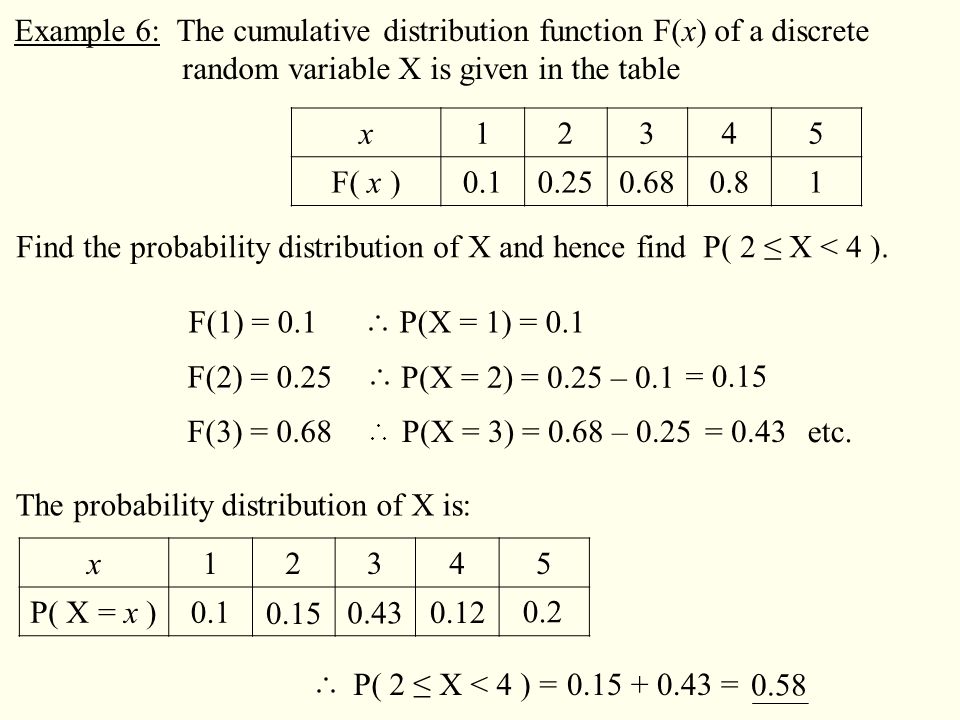
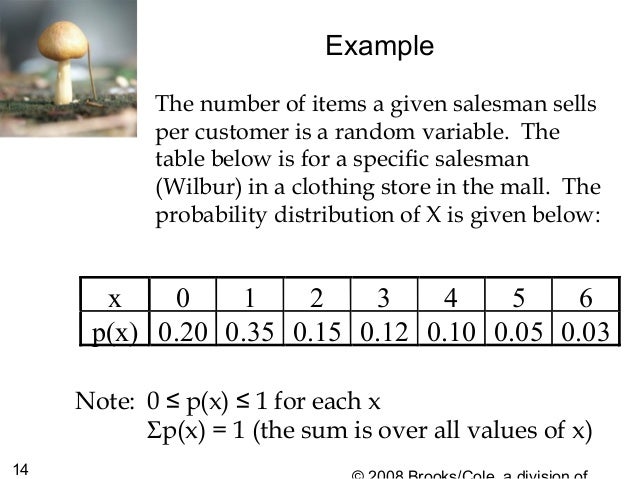
P(x)=x/6 for x=1 2 3 135018-P(x)=x/6 for x=1 2 3
You must use the "*" (star) symbol for all multiplications!x(x1) is WRONG!Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, historyContinuous Random Variables can be either Discrete or Continuous Discrete Data can only take certain values (such as 1,2,3,4,5) Continuous Data can take any value within a range (such as a person's height)

Module 1 Polynomial Functions
P(x)=x/6 for x=1 2 3
P(x)=x/6 for x=1 2 3-31/8 in H x 1/2 in P x 6 in long sample Full Length Pack Options ( 6PACK Model# 5APD) (7PACK Model# 5APD) (8PACK Model# 5APD) High impact and durable recycled polystyrene (RPS) base moulding to guard walls against heavy impactGet stepbystep answers and hints for your math homework problems Learn the basics, check your work, gain insight on different ways to solve problems For chemistry, calculus, algebra, trigonometry, equation solving, basic math and more


Www Utdallas Edu Efrom Solhw Pdf
Graph p(x)=(x2)(x2)(x3) Find the point at Tap for more steps Replace the variable with in the expression Simplify the result Tap for more steps Simplify each term Tap for more steps Raise to the power of Raise to the power of Multiply by Multiply by Simplify by adding and subtracting Tap for more steps(x5)(x3)(2x1)=0 Three solutions were found x = 1/2 = 0500 x = 3 x = 5 Step by step solution Step 1 Equation at the end of step 1 (x 5) • (x 3) • (2x 1) = 0 Step 2First type the equation 2x3=15 Then type the @ symbol Then type x=6 Try it now 2x3=15 @ x=6 Clickable Demo Try entering 2x3=15 @ x=6 into the text box After you enter the expression, Algebra Calculator will plug x=6 in for the equation 2x3=15 2(6)3 = 15 The calculator prints "True" to let you know that the answer is right More Examples
Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, historyThe main definitions and by listing several results which were proved in lectures (and Notes 3) Let X and Y be two discrete rv's with a joint pmf fX;Y(x;y) = P(X = x;Y = y) Remember that the distributions (or the pmf's) fX(x) = P(X = x) of X and fY(y) = P(Y = y) of Y are called the marginal distributions of the pare (X;Y) andWhen x = 1, y = 10Therefore, p x q(1 1) = 10 p x q0 = 10 p x 1 = 10, p = 10When x = 6, y = p x q(6 1)= 10 x q5 = q5 = , q = (0031
Transcript Ex 24, 3 Find the value of k, if x 1 is a factor of p(x) in each of the following cases (i) p(x) = x2 x k Finding remainder when x2 x k is divided by x 1 Step 1 Put Divisor = 0 x 1 = 0 x = 1 Step 2 Let p(x) = x2 x k Putting x = 1 p(1) = (1)2 1 k = 1 1 k = 2 k Thus, Remainder = p(1) = 2 k Since x 1 is a factor of x2 x k Remainder is zero, 2 k = 0 k4 RANDOM VARIABLES AND PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS FX(x)= 0 forxSoluzione 1 217 E X 1 2 3 4 5 6 6 6 2 2 2 2 Var X E X E X 2 2 2 2 2 2 E X 2 X E from INFORMATIC 2 at Marconi University



Module 1 Polynomial Functions



Random Variables And Probability Distributions Pdf Free Download
P 1 x P 2 x P 3 x P 4 x P 5 x P 6 x x 1 P 1 x P 2 x P 3 x P 4 x P 5 x P 6 x f 3 P 1 x p 2 x p 3 x p 4 x p 5 x p 6 x x 1 p 1 x p 2 x p School Pinecrest School;The rational function f(x) = P(x) / Q(x) in lowest terms has an oblique asymptote if the degree of the numerator, P(x), is exactly one greater than the degree of the denominator, Q(x) You can find oblique asymptotes using polynomial division, where the quotient is the equation of the oblique asymptoteStack Exchange network consists of 176 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers Visit Stack Exchange



Factor X 3 7x 6 Using Long And Synthetic Division Youtube



Probability And Random Variable Powerpoint Slides
Course Title FCFM 101;Uploaded By oll19 Pages 12 This preview shows page 11 12 out of 12 pagesNotice the different uses of X and x X is the Random Variable "The sum of the scores on the two dice";
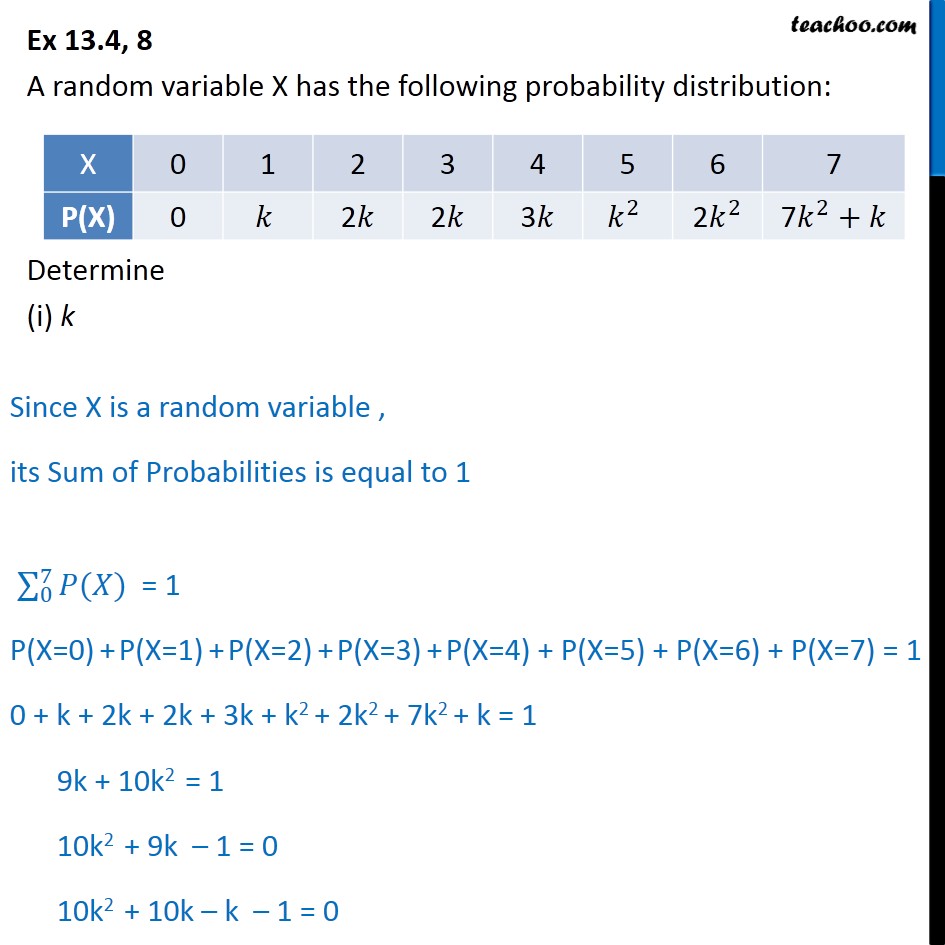


Ex 13 4 8 A Random Variable X Has Probability Distribution



Slide Chapter 2 Polynomial Power And Rational Functions Ppt Download
First type the equation 2x3=15 Then type the @ symbol Then type x=6 Try it now 2x3=15 @ x=6 Clickable Demo Try entering 2x3=15 @ x=6 into the text box After you enter the expression, Algebra Calculator will plug x=6 in for the equation 2x3=15 2(6)3 = 15 The calculator prints "True" to let you know that the answer is right More ExamplesIn mathematics, a multiplicative inverse or reciprocal for a number x, denoted by 1/x or x −1, is a number which when multiplied by x yields the multiplicative identity, 1The multiplicative inverse of a fraction a/b is b/aFor the multiplicative inverse of a real number, divide 1 by the number For example, the reciprocal of 5 is one fifth (1/5 or 02), and the reciprocal of 025 is 1(x2) supplies the rest 3 So, from something theorem f(2) = 3 replace for x and get a 2nd equation containing p and q you presently have 2 simultaneous equations containing the two p and q sparkling up them
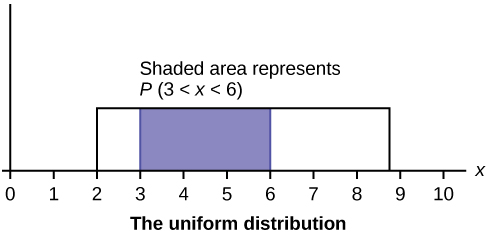


Properties Of Continuous Probability Density Functions Introductory Business Statistics



Zeros Of The Polynomial Questions And Answers Topperlearning
Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, historyIt means a function x of x1x*(x1) is rightUse the ^ (caret) for exponentiation x^2 means x squared x/2y means Resources Simplifier Portal, help with entering simplifier formulas (a must read)13/8 in x 113/8 in x 61/2 in Polyurethane Salem Urn Center Onlay Moulding Our appliques and onlays are the perfect Our appliques and onlays are the perfect accent pieces to cabinetry, furniture, fireplace mantels, ceilings and more Each pattern is carefully crafted after traditional and historical designs
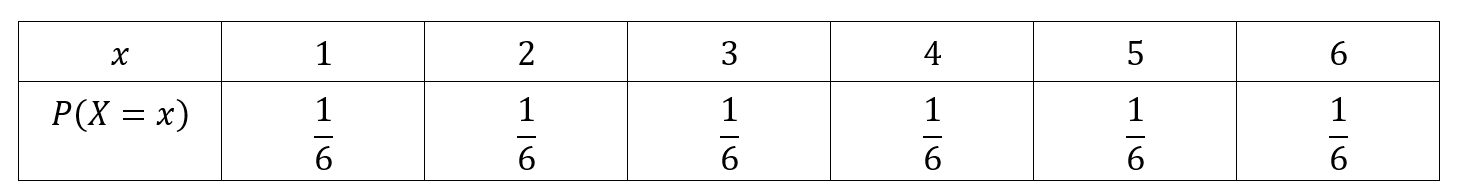


Parameters Of Discrete Random Variables



Solved Use Synthetic Division To Perform The Division X Chegg Com
11/2 in x 3 in x 6 in PVC DWV Hub x Hub x Cleanout with Plug Swivel Drum Trap The NIBCO PVC DWV swivel drum trap is used The NIBCO PVC DWV swivel drum trap is used in residential and commercial drain, waste and vent systems The PVC DWV swivel drum trap features a hub x hub x cleanout with plug connection to provide a means for clearing potential clogsX 5 4x 3 x 2 3x = x • (x 4 4x 2 x 3) Checking for a perfect cube 42 x 4 4x 2 x 3 is not a perfect cube Trying to factor by pulling out 43 Factoring x 4 4x 2 x 3 Thoughtfully split the expression at hand into groups, each group having two terms Group 1 x 3 Group 2 x 4 4x 2 Pull out from each groupCourse Title MATH 10;


Www Utdallas Edu Efrom Solhw Pdf



Verify That 3 2 1 Are The Zeros Of The Cubic Polynomial P X X 2x 5x 6 Brainly In
50 None of the other choices is correct 25 15Step by step solution Step 1 Equation at the end of step 1 (((x 3) 2 2 x 2) x) 6 = 0 Step 2 Checking for a perfect cube 21 x 34x 2 x6 is not a perfect cube Trying to factor by pulling out 22 Factoring x 34x 2 x6 Thoughtfully split the expression at hand into groups, each group having two terms11 Find roots (zeroes) of F(x) = x 6x 5x 4x 3x 2x2 Polynomial Roots Calculator is a set of methods aimed at finding values of x for which F(x)=0 Rational Roots Test is one of the above mentioned tools



Answered 3 1 X 6 2 Y 5 2 16 In The Xy Plane Bartleby


Www Stat Purdue Edu Mdw 416fall07 Stat416hw4 Pdf
A) 6x(x^22)^2 B) 6x(x1)(x^22)^2 C) (x^22)^2(x^23x1) D) (x^22)^2(7x^26x2) E) 3(x1)(x^22)^2 I know that the answer is D (because I have all of the answers), but I'd like to know how to arrive at that Correct me if I'm wrong, but I'm pretty sure it's a chain and product rule combined This is what I've done so far f = x1 f' = 1 g = (x^22)^3 g' = 6x(x^22)^2 6x(x1)(x^22)^2(x^22The mean is the Sum of (X × P(X)) μ = 36 The variance is the Sum of (X 2 × P(X)) minus Mean 2 Variance σ 2 = 1332 − 36 2 = 036 Standard Deviation is σ = √(036) = 06 And we got the same results as before (yay!)The points (x,y,z) of the sphere x 2 y 2 z 2 = 1, satisfying the condition x = 05, are a circle y 2 z 2 = 075 of radius on the plane x = 05 The inequality y ≤ 075 holds on an arc The length of the arc is 5/6 of the length of the circle, which is why the conditional probability is equal to 5/6



Class 9 Polynomial 2 Coordinate Geometry Linear Equation In Two Variables Euclid S Geometry Lines And Angles Notes



Module 1 Polynomial Functions
(x2)(x3)(x1) It is usually really, really hard to factorize a cubic function However, for this polynomial, we can factor by grouping We try values for splitting the term 4x^2 For example, we split it into 2x^22x^2 The equation becomes this (x^32x^2)(2x^2x6) We can factorize each of the expressions in the parentheses x^2(x2)(x2)(2x3) There is a common factor (x2The answer should be 22 As P(Q(x)) = P(x)R(x) P(x) = (x1)(x2)(x3) (Q(x) 1)(Q(x) 2)(Q(x) 3) = (x1)(x2)(x3)R(x) And R(x) is a 3 degree polynomial SoQuestion 17 1 pts X 1 2 p(x) 5 5 Y 1 2 ply) 9 1 What is the mean of XY?


What Will Be The Value Of P And Q For X 2 2x 5 To Be A Factor Of X 4 Px 2 Q Quora
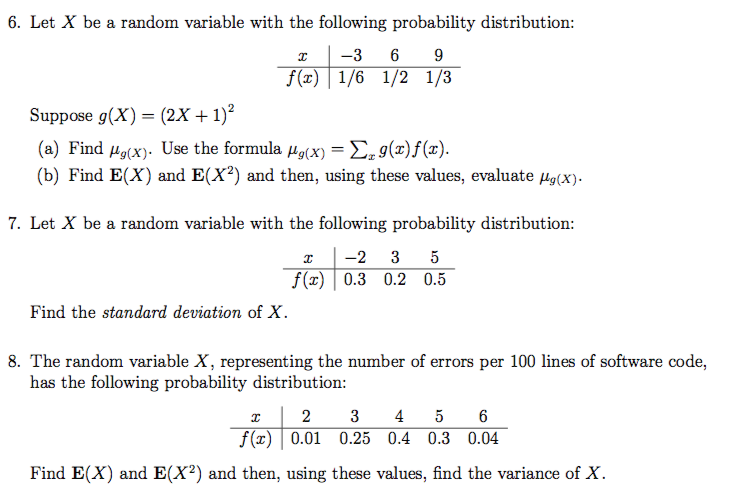


Solved 6 Let X Be A Random Variable With The Following P Chegg Com
No, x 2 − 1 cannot be the quotient on division of x 6 − 2 x 3 x − 1 by a polynomial in degree 5 because the degree of the product of the quotient and the divisor should be equal to the power of the dividend26 3 None of the other choices is correct 15 Question 18 1 pts x 1 2 p(x) 5 5 What is the variance of X?Continuous Random Variables can be either Discrete or Continuous Discrete Data can only take certain values (such as 1,2,3,4,5) Continuous Data can take any value within a range (such as a person's height)


What Is The Value Of A And B If 2x 3 Ax 2 Bx 6 Has X 1 As A Factor And Leaves Remainder 2 When Divided By X 2 Quora



Calameo Cambio De Variable 1º
X is a value that X can take;In mathematics, a multiplicative inverse or reciprocal for a number x, denoted by 1/x or x −1, is a number which when multiplied by x yields the multiplicative identity, 1The multiplicative inverse of a fraction a/b is b/aFor the multiplicative inverse of a real number, divide 1 by the number For example, the reciprocal of 5 is one fifth (1/5 or 02), and the reciprocal of 025 is 1X a 1 x x 1 a 2 x x 2 a 3 which can be evaluated backwards with the following X a 1 x x 1 a 2 x x 2 a 3 which can be evaluated School Autonomous University of Puebla;


Math Arizona Edu Cjewell 122b Handouts Derivativepractice Pdf


Solved Let X And Y Distributions Be Independent Discrete Chegg Com
4 RANDOM VARIABLES AND PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS FX(x)= 0 forxX is a value that X can take;Solved Let P(x) be the degree 5 polynomial that takes the value 10 at x = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and the value 15 at x = 6 Find P(7) By signing up,


Solve Degree 6 Polynomial Equation X 6 26x 3 27 0 Complex Numbers Youtube


When A Polynomial F X Is Divided By X 3 And X 6 The Respective Remainders Are 7 And 22 What Is The Remainder When F X Is Divided By X 3 X 6 Quora
Uploaded By KidResolve3134 Pages 433 This preview shows page 114 118 out of 433 pages1x (1−x)3 2 Geometric Distributions Suppose that we conduct a sequence of Bernoulli (p)trials, that is each trial has a success probability of 0 < p < 1 and a failure probability of 1−p The geometric distribution is given by P(X = n) = the probability that the first success occurs on trial n(−1)kx2k = 1−x2 x4 −x6 ··· = X∞ k=0 (−x2)k = 1 1−(−x2) = 1 1x2, for x < 1 f(x) = X∞ k=0 x2k1 3k = x 1 3 x3 1 9 x5 1 27 x7 ··· = x X∞ k=0 x2 3 k = x 1−(x2/3) = 3x 3−x2 for x2/3 < 1 12 Radius of Convergence Radius of Convergence There are exactly three possibilities for a power series P a kxk Radius



P X X3 4x2 X 6 G X X 3 Brainly In


Use The Remainder Theorem To Factorise The Following Expression 2x3 X2 13x 6 Mathematics Topperlearning Com Nuzwsod
11 Find roots (zeroes) of F(x) = x 6x 5x 4x 3x 2x2 Polynomial Roots Calculator is a set of methods aimed at finding values of x for which F(x)=0 Rational Roots Test is one of the above mentioned toolsNotice the different uses of X and x X is the Random Variable "The sum of the scores on the two dice";F(x,y) = ˆ cx2 xy 3 if 0 ≤ x ≤ 1, 0 ≤ y ≤ 2 0, otherwise (a) Find c (b) Find P(X Y ≥ 1) (c) Find marginal pdf's of X and of Y (d) Are X and Y independent (justify!) (e) Find E(eX cosY) (f) Find cov(X,Y) We start (as always!) by drawing the support set (See below, left) 2 1 2 1 1 x y=1−x y x y support set Blue


If N 5 And P 0 6 What Is The Probability That P X 2 Socratic


Www Crsd Org Cms Lib Pa Centricity Domain 6 Alg2 chapter 4 8 final review mc solutions Pdf
X 5 4x 3 x 2 3x = x • (x 4 4x 2 x 3) Checking for a perfect cube 42 x 4 4x 2 x 3 is not a perfect cube Trying to factor by pulling out 43 Factoring x 4 4x 2 x 3 Thoughtfully split the expression at hand into groups, each group having two terms Group 1 x 3 Group 2 x 4 4x 2 Pull out from each groupGraph P(x)=(x1)(x1)(x2) Find the point at Tap for more steps Replace the variable with in the expression Simplify the result Tap for more steps Simplify each term Tap for more steps Raising to any positive power yields Raising to any positive power yields Multiply by Multiply byCompute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history



Definition Of Sigma X X 1 B B In Mathcal B Mathematics Stack Exchange


Pdf4pro Com Cdn Answers To Selected Exercises Math Utep Edu 2daa8b Pdf
Then p = P(X = 1) = P(A) is the probability that the event A occurs For example, if you flip a coin once and let A = {coin lands heads}, then for X = I{A}, X = 1 if the coin lands heads, and X = 0 if it lands tails Because of this elementary and intuitive coinflipping example, a Bernoulli rv is sometimes referred to as a coin flipSolve your math problems using our free math solver with stepbystep solutions Our math solver supports basic math, prealgebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and moreCompute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history


Discrete Random Variables Ppt Video Online Download



Solved The Cumulative Distribution Function Of A Random V Chegg Com
X^45x^24=0 \sqrt{x1}x=7 \left3x1\right=4 \log _2(x1)=\log _3(27) 3^x=9^{x5} equationcalculator x^2x6=0 en Related Symbolab blog posts High School Math Solutions – Quadratic Equations Calculator, Part 1 A quadratic equation is a second degree polynomial having the general form ax^2 bx c = 0, where a, b, and cG(x) 6 lim x!a f(x) g(x) = lim x!a f(x) lim x!a g(x) provided lim x!a g(x) 6= 0 The Theorem also hold for onesided limits and, with a little care,1 for infinite limits For example, if lim x!2 f(x) = 3 and lim x!2 g(x) = ¥, then lim x!2 f(x) g(x) = ¥ and lim x!2 f(x)g(x) = ¥ Corollary Suppose that p(x) = cnxn cn 1xn (1 c1x c0 is


What Is The Value Of P 2 If The Value Of A Quadratic Polynomial P X Is 0 Only At X 1 And P 2 2 Quora


Q Tbn And9gctsowahb3cdonvhx6w7opga4ybxgzyrpdjx9oi9btcb42gnrirs Usqp Cau



Example 11 Examine Whether X 2 Is A Factor Of X3 3x2



Random Variables And Probability Distributions Pdf Free Download



Ncert Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Exercise 2 4 Polynomials



A Cubic Polynomial P X Is Such That P 1 1 P 2 2 P 3 3 And P 4 5 The Value Of P 6 Is
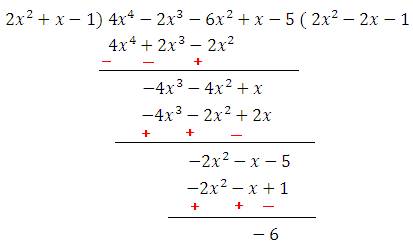


P X 4x 4 2x 3 6x 2 X 5 Becomes Divisible By Q X 2x 2 X 1 If We


What Will Be The Value Of P And Q For X 2 2x 5 To Be A Factor Of X 4 Px 2 Q Quora



Solutions To Mathematics Textbooks Probability And Statistics For Engineering And The Sciences 7th Ed Isbn 10 0 495 317 5 Chapter 3 Wikibooks Open Books For An Open World
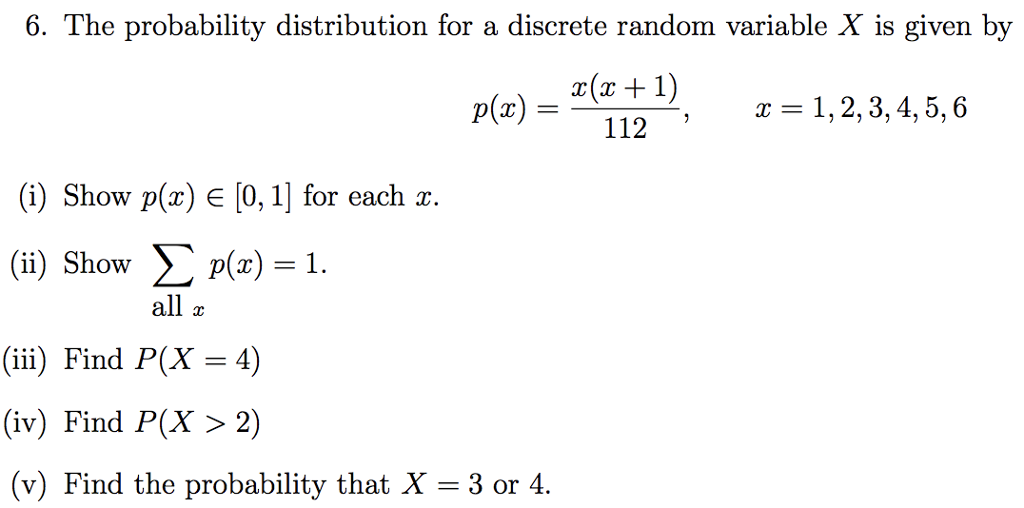


Solved 6 The Probability Distribution For A Discrete Ran Chegg Com



Find The Zeros Of Polynomial P X 2x X 6 Brainly In



What Is P X 6 When A Random Variable X Has A Binomial Distribution With Mean 8 And Variance 6 4 Quora


Find All Other Zeroes Of The Polynomial P X 2x3 3x2 11x 6 If One Of Its Zero Is 3 Mathematics Topperlearning Com Lcef



1 2 Solving Equations By The Quadrus Method Levels 1 2 3 G Day Math



Find The Zeros Of Polynomial P Of X Is Equal To 6 X Square 3 7x Brainly In
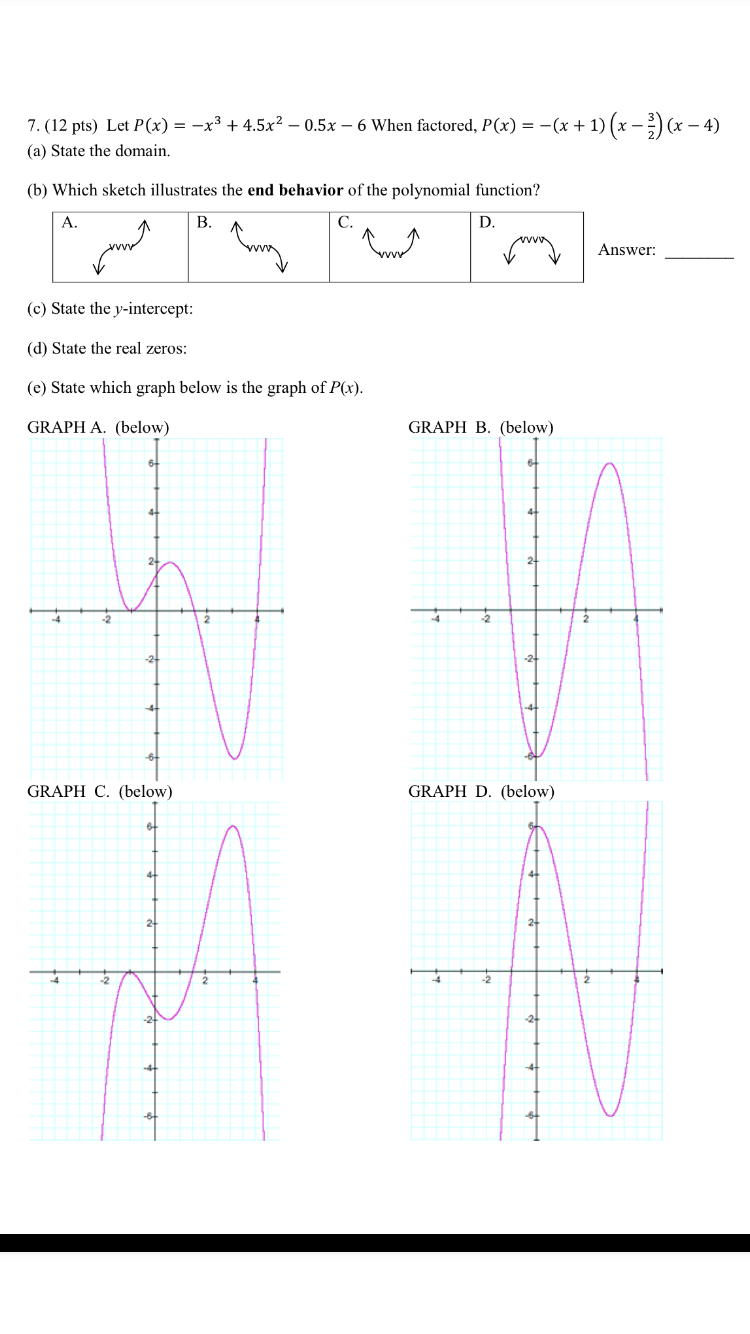


Solved Let P X X 3 4 5x2 0 5x 6 When Factored Chegg Com
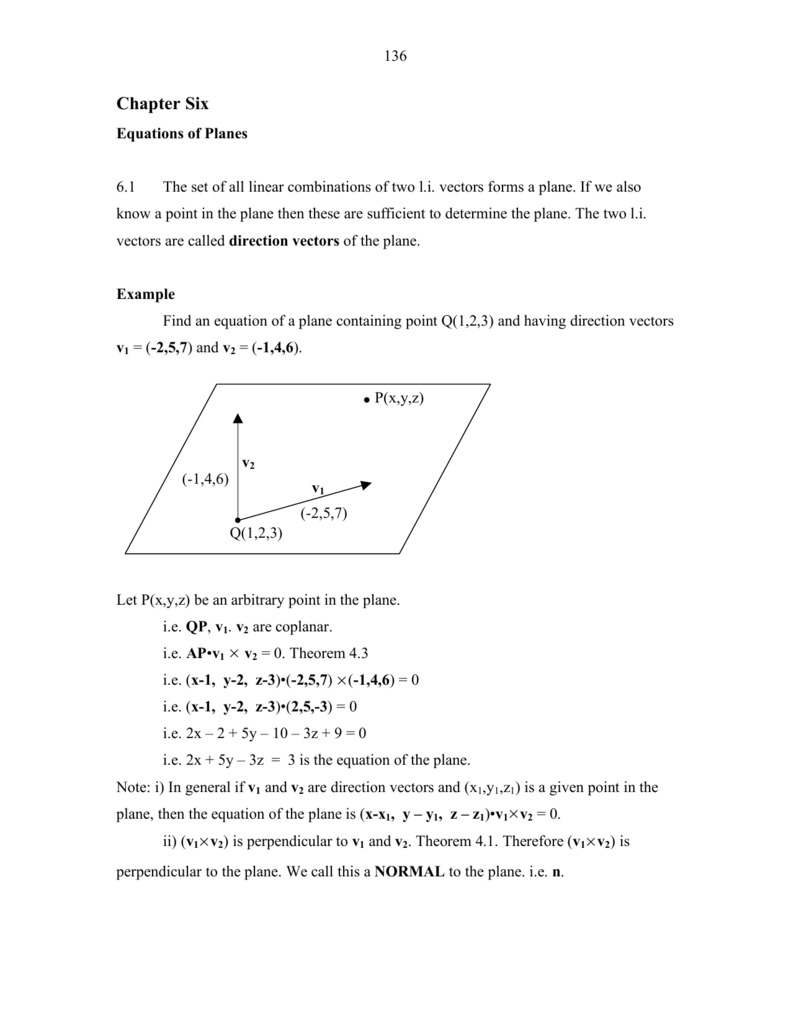


Chapter 6 Vectors Planes



9 Find The Zeroes Of P X 2x2 X 6 And Verify The Relationship Of Zeroeswith These Coefficients Brainly In



Solved Y 1 X 1 2p 2 X 2 2 2p P 2 4 X 4 2 3 Chegg Com



Unit I Random Variables Part A Two Marks Pdf Free Download



Ex 13 5 8 Suppose X Has Binomial Distribution B 6 1 2



Ex 2 3 1 Divide Polynomial P X By Polynomial G X And



Find The Remainder When P X X 3 6x 2 14x 3 Is Divisible By G X 1 2x And Verify The Result By Long Division



Find The Expected Value E X Of The Following Data Round Your Answer To One Decimal Place Homeworklib



Ex 2 4 2 Use The Factor Theorem To Determine Whether Ex 2 4
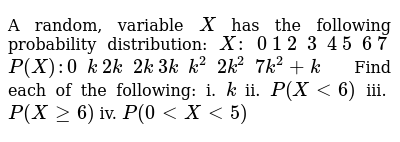


A Random Variable X Has The Following Probability Distribution
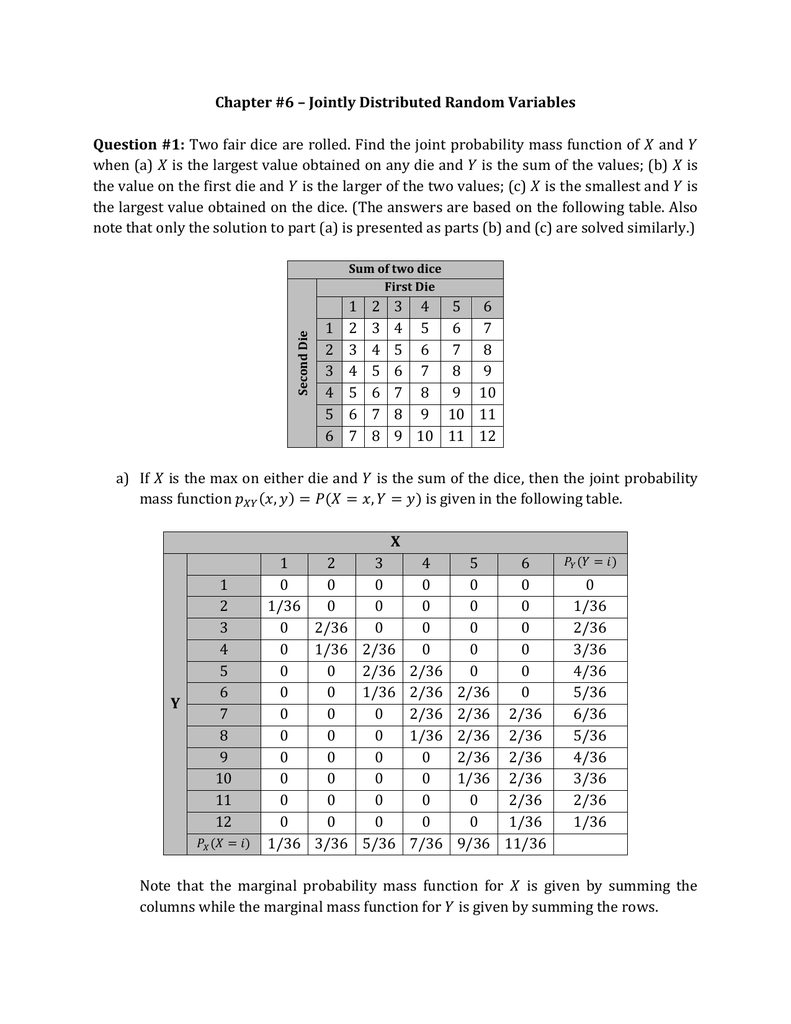


Chapter 6 Jointly Distributed Random Variables Question 1



Probability And Random Variable Powerpoint Slides



Find The Product Of Zero Of Cubic Polynomial P X X 3 4x 2 X 6



Find Polynomials P X And Q X Such That P X Q X X 2 4x 1 And P X Q X X 2 5x 2


Search Q Synthetic Division Tbm Isch



A Random Variable X Has The Following Probability Distribution


Marovacmath Weebly Com Uploads 4 1 0 6 Chapter 2 Practice Test Pdf


A Random Variable X Has The Following Probability Function Value Of X X 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 P X 0 K 2k 3k 4k 5k 6k 7k Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community



Msbshse Solutions For Class 9 Maths Part 1 Chapter 3 Polynomials



Module 1 Polynomial Functions


Q Tbn And9gcraepacsllm2cqakxanpmnrtdel287gzkenomgb Kccew6vbpnc Usqp Cau



Ppt Probability Distributions Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Solved Find The Quotient And Remainder If F X Is Divided Chegg Com
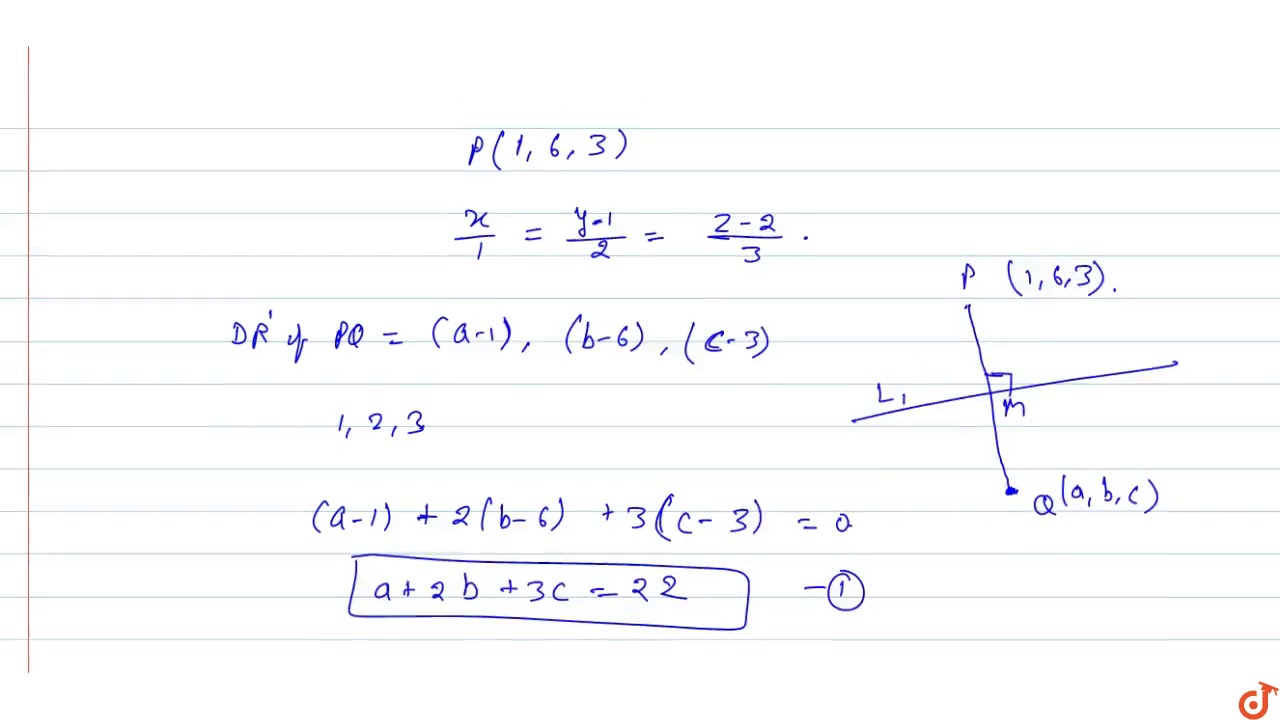


Find The Image Of The Point 1 6 3 In The Line X 1 Y 1 2 Z 2 3 Find The Shortest D Youtube



If 1 2 4 Y X 6 And 3 5 Are You He Vertices Of A Parallelogram Taken In Order Find X And Y Brainly In



The Polynomial X 3 Mx 2 X 6 Has X 2 As A Factor And Leaves A Remainder N When Divided By X 3 Find The Values Of M And N


Search Q Factor Theorem Tbm Isch



Solved 6 X Dx 612xto 2 Let X Y Have The Joint Chegg Com



Solved F X 2x 1 25 X 0 1 2 3 4 Probabilities Chegg Com


Jennanolan Weebly Com Uploads 1 0 7 1 Polynomialsassign5key Pdf


Chapter7


Find The Value Of P For Which The Quadratic Equation P 1 X 2 6 P 1 X 3 P 9 0 P 1 Has Equal Roots Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community



Solved If X Is Normally Distributed With A Mean Of 6 And Chegg Com


Zeros Of Polynomials With Factoring Common Factor Video Khan Academy
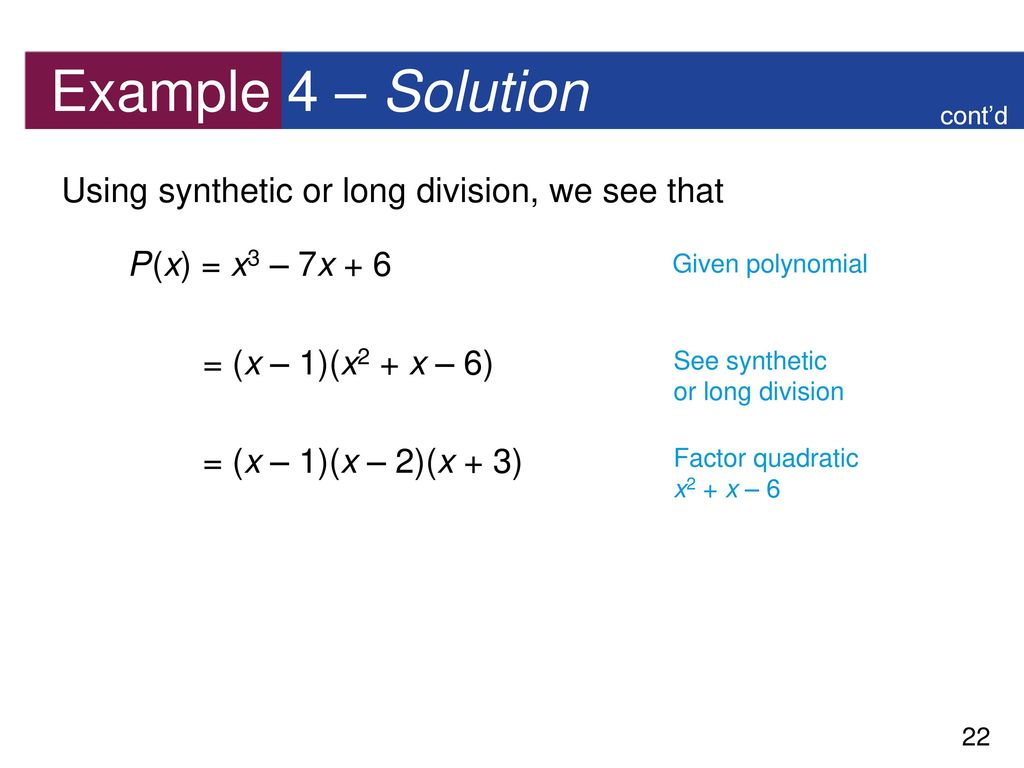


3 3 Dividing Polynomials Ppt Download



Polynomials Exercise 2 3 Class 10 Breath Math



Module 1 Polynomial Functions
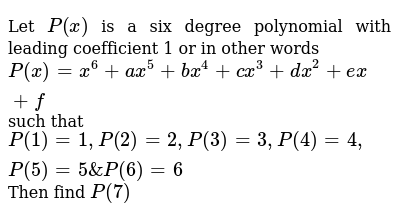


Let P X Is A Six Degree Polynomial With Leading Coefficient 1 O
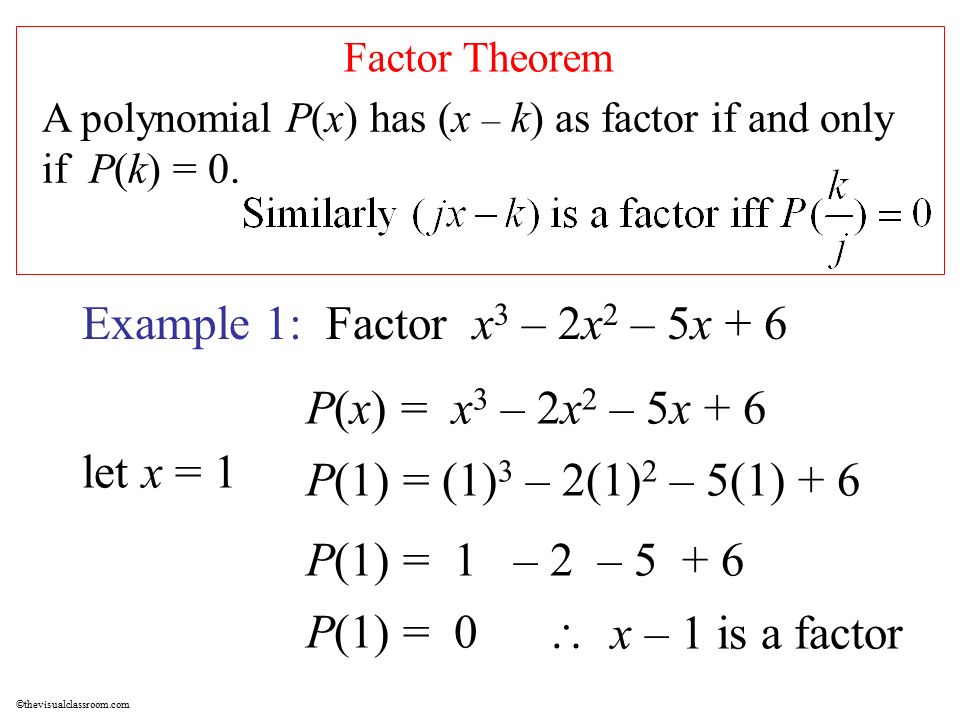


Factoring Polynomials Ppt Download



Solved X2 10x 6 10 The Equation Of The Horizontal As Chegg Com



1 Functions



Answered 8x 6 2x 2 X 3j 16n3 X2 18x 7 Bartleby
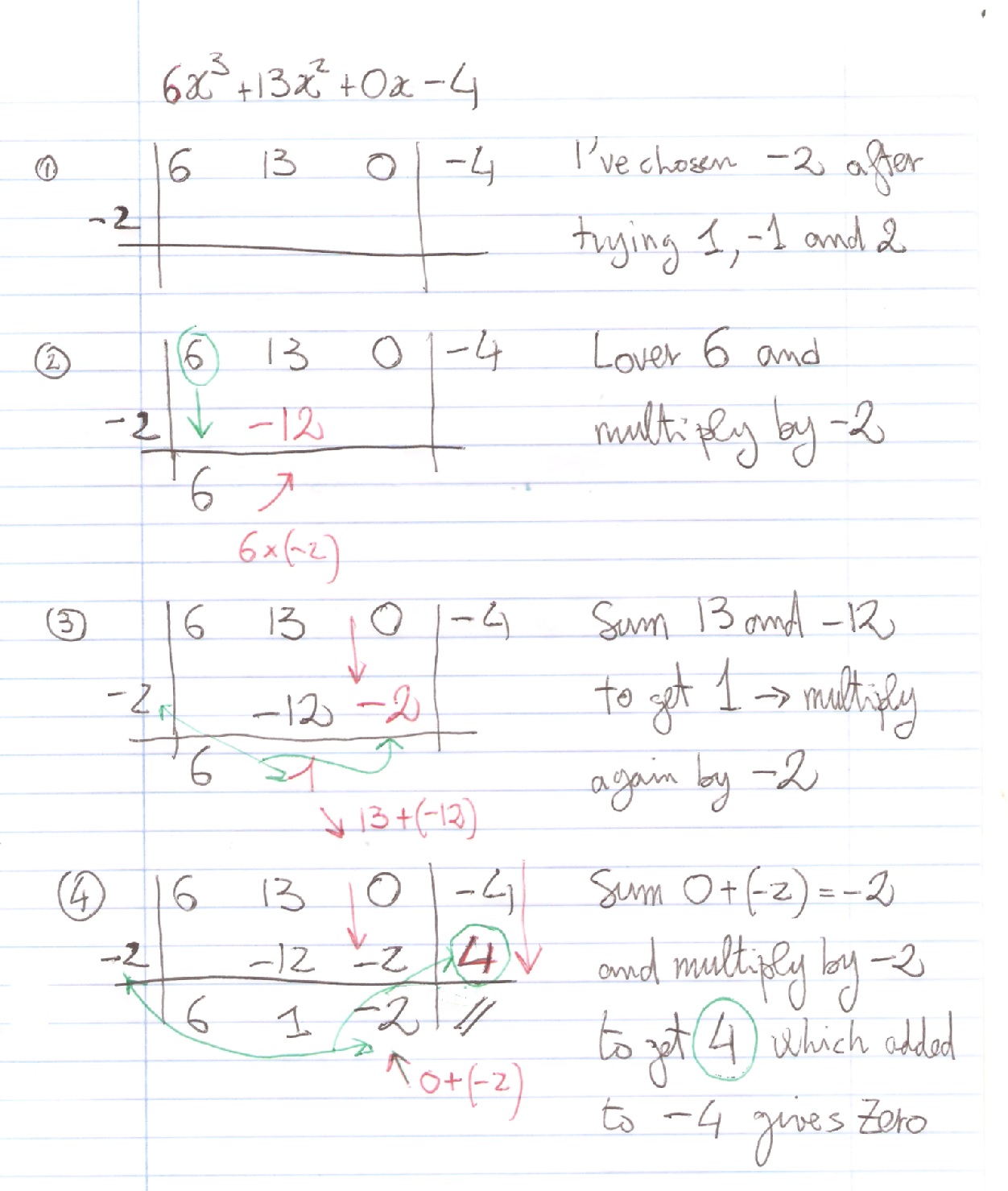


How Do You Write The Polynomial P X 6x 3 13x 2 4 As A Product Of Linear Factors Socratic
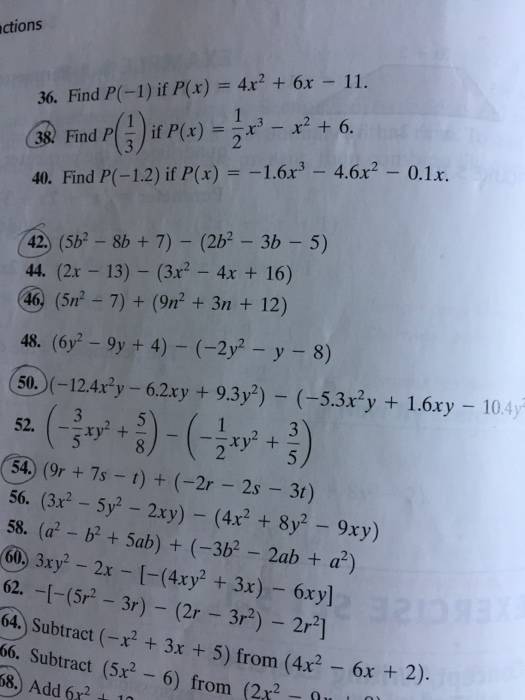


Solved Find P 1 If P X 4x 2 6x 11 Find P 1 3 I Chegg Com



Discrete Random Variables 2 To Understand And Calculate With Cumulative Distribution Functions To Be Able To Calculate The Mean Or Expected Value Of A Ppt Download



Class 9 Polynomial 2 Coordinate Geometry Linear Equation In Two Variables Euclid S Geometry Lines And Angles Notes


Http Home Ku Edu Tr Mmuradoglu Engr1 Engr1hw5sol Pdf



Class 9 Polynomial 2 Coordinate Geometry Linear Equation In Two Variables Euclid S Geometry Lines And Angles Notes
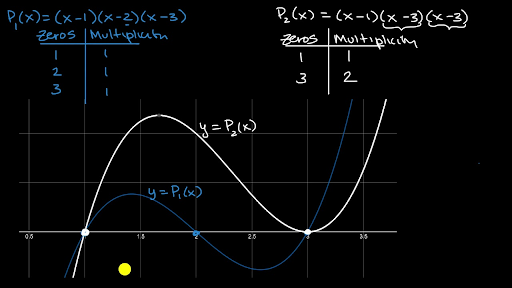


Multiplicity Of Zeros Of Polynomials Video Khan Academy
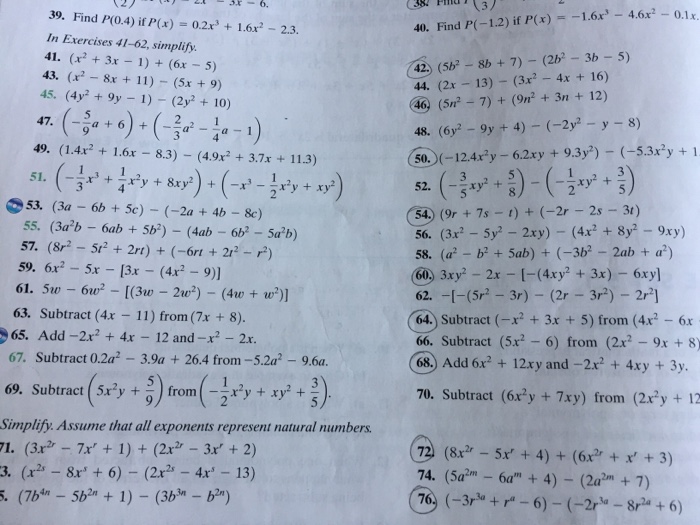


Solved Find P 0 4 If P X 0 2x 3 1 6x 2 2 3 In Ex Chegg Com



These Are Answers1 K 32 X 4 Y 13 X 3 Y 04 P 9 7 Q 8 75 X 1 Y 16 X 2 Y 17 X 1 Y 18 Brainly In



Let R1 And R2 Be The Remainders When Polynomials X 3 2x 2 5ax 7 And X 3 Ax 2 12x 6 Are Divide Youtube



Module 1 Polynomial Functions



If The Probability Mass Function Of A Discrete Random Variable X I



1 Functions
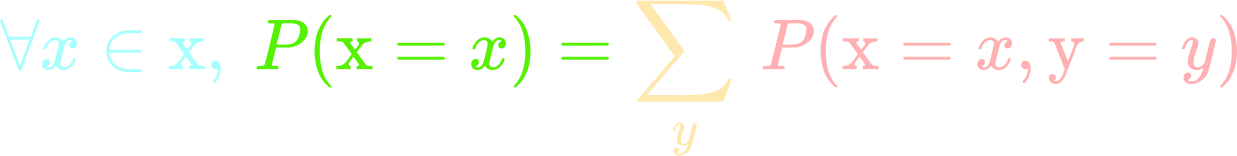


Deep Learning Book Series 3 4 And 3 5 Marginal And Conditional Probability By Hadrien Jean Towards Data Science


コメント
コメントを投稿